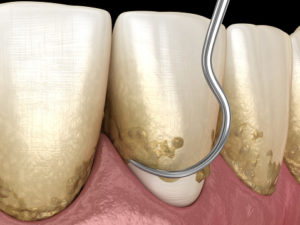
Plaque and Tartar
Plaque can lead to gingivitis by first forming on your teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of mainly bacteria that accumulates on your teeth when starches and sugars in food interact with the bacteria in your mouth. Plaque requires to be removed daily because it forms and re-forms quickly. If plaque is left untouched, it can harden under the gum line and turn into tartar. When plaque becomes tartar, it is more difficult to remove and creates a protective shield for bacteria causing irritation along the gum line. Professional dental cleaning will be needed to remove tartar. The longer plaque and tartar remain on your teeth, the more the gingiva will get irritated and inflamed, making it bleed more easily. Even though the gums are inflamed and irritated with gingivitis, the teeth are firmly still in place and no bone or other tissue damage has yet occurred.
Gingivitis Can Lead to Periodontal Disease
When gingivitis is left untreated, it can lead to tooth decay and periodontitis or advanced gum and teeth disease. As gingivitis is prolonged, it progresses to affecting and damaging more of the gum tissues and the bones. The inner layer of the gum and bone can pull away from the teeth and form pockets. The small spaces between the teeth and gums collect debris and can get infected. The body’s immune system will fight the bacteria as the plaque spreads and grows below the gum line. The bacteria in plaque produce toxins as well as the “good” infection fighting cells of the immune system can release enzymes that break down the bone and connective tissues that hold the teeth. Once the connective tissues and bones are destroyed, the teeth can no longer be anchored in place, they become loose, and the tooth is lost. The leading cause of tooth loss is gum disease in adults. Symptoms of gum disease are: bleeding gums during brushing, inflamed (red, swollen, tender) gums, bad breath or taste in the mouth, receding gums, deep pockets formed between teeth and gums, or loose teeth.
Good oral habits like brushing at least twice daily, flossing daily, and getting regular dental checkups can prevent and reverse gingivitis. If you would like to schedule a dental cleaning contact California Dental Group at 800-407-0161 to schedule an appointment.

